Disclosure based on TCFD recommendations

In November 2021, we announced our support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). We disclose information on business risks and opportunities associated with climate change and their financial impact based on this TCFD framework.
- *This disclosure applies to the Company and to domestic subsidiaries.
Status of TCFD scenario analysis implementation
| FY2022 | FY2023 | |
|---|---|---|
| Details |
|
|
Governance
Management structure for addressing climate change
- Mitsubishi Steel's Sustainability Committee (chaired by the President & CEO) deliberates on materialities related to sustainability, including climate change. In principle, the Board of Directors deliberates on sustainability on a monthly basis.
- We have established a Companywide management structure to promote sustainability through various means, including assessing and managing climate change risks and opportunities. This structure includes, as organizations under the umbrella of the Sustainability Committee, the Global Environment Committee, Carbon Neutral Committee, and ESG Subcommittee.
- In November 2021, we announced our support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). In FY2022, we carried out an initial review of risks, opportunities, and responses related to climate change and formulated a roadmap to achieve carbon neutrality by FY2050. In FY2023, we reassessed risks and opportunities by business division; carried out scenario analysis and assessments of financial impact; and reviewed the responses once again.
Status of activities to address issues related to climate change in major meeting bodies
| Sustainability Committee | Carbon Neutral Committee | ESG Subcommittee | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roles in addressing climate change issues | Implementing TCFD scenario analysis and formulating policies for addressing climate change and details thereof | Drafting and executing policies, plans, and targets for efforts to achieve carbon neutrality | Collecting external information on climate change and communicating this information internally and externally |
| Details of FY2022 activities related to climate change | Held 10 meetings in 2022, including five meetings for discussions of agenda items related to climate change. | Set annual targets for CO2emissions through FY2025; formulated FY2023-2030 plans and adopted ICP regarding capital investment, advanced study of Scope 3 emissions calculations, and overseas initiatives. | Reviewed risks and opportunities related to the effects of climate change anew and revised responses once again based on scenario analysis and assessments of financial impact to enhance disclosures based on TCFD recommendations. |
For information on the sustainability structure, please refer to the sustainability promotion system.
Strategy
Scenario analysis assumptions
- The Company carried out scenario analysis of its businesses in Japan over the course of the timelines leading to 2030 and 2050 based on two scenarios: a scenario in which global measures to address climate change succeed in keeping the increase in average temperatures by the end of the century to less than 1.5℃ (the 1.5℃ Scenario, in which mainly transition risks are manifested due to factors such as regulations related to climate change) and a scenario in which such measures remain inadequate (the 4℃ Scenario, in which mainly physical risks are manifested due to factors such as increasing natural disasters).
- Scenarios published by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other authorities were referred to in the scenario analysis. The 1.5℃ Scenario and the 4℃ Scenario are summarized below.
| Risks | Vision of society under each scenario | External scenarios referred to in scenario analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃ Scenario (transition risks) |
| International Energy Agency (IEA) World Energy Outlook Report 2022
|
| 4℃ Scenario (physical risks) |
|
- *1APS: Announced Pledges Scenario, NZE: Net Zero Emissions Scenario, SDS : Sustainable Development Scenario
- *2SSP5: Scenario under which global economic development continues to depend on energy from fossil fuels; RCP8.5: high emissions scenario under which emissions continue to increase throughout the 21st century
Risks, opportunities, and corresponding timelines and impact
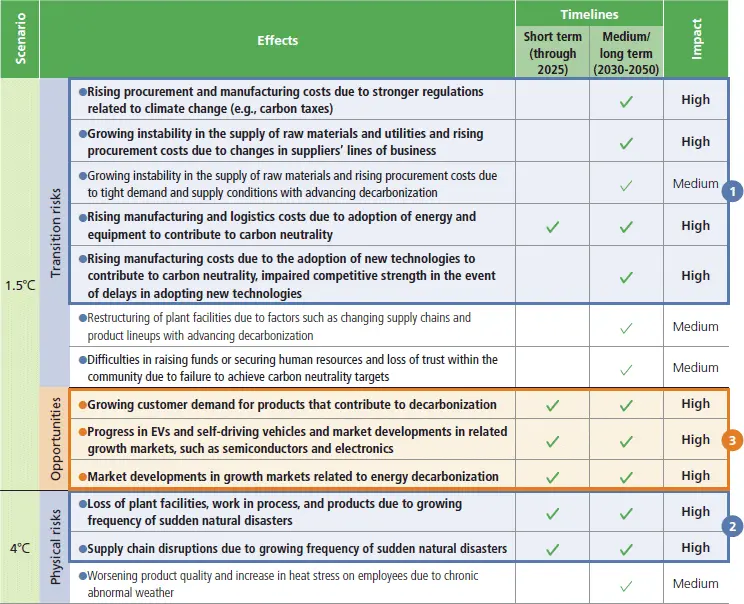
Responses to transition risks and opportunities
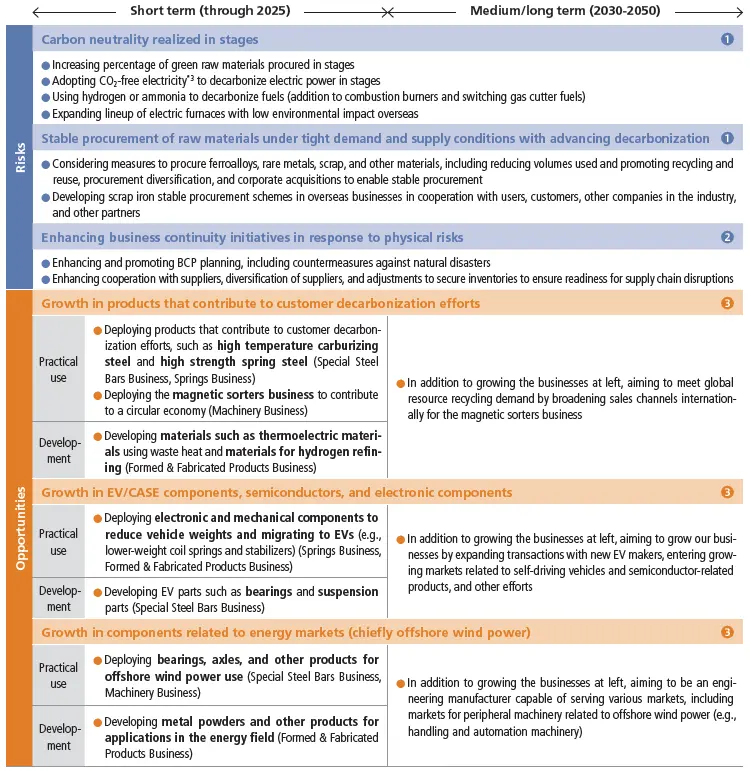
- *3Certified non-fossil-fuel electricity
Strategic resilience
- Since climate change can cause major impacts on our businesses, both in the form of risks and opportunities, we recognize it as a key management issue for Mitsubishi Steel's medium-to long-term growth.
- Under the 1.5℃ Scenario, in which global measures to address climate change are successful, we anticipate that climate change regulations, including carbon taxes, would be enhanced. Thus, efforts toward carbon neutrality would be essential in areas such as raw materials and manufacturing processes. While striving to realize carbon neutrality in stages, we will enhance sales of products in new growth markets created by progress with decarbonization (i.e., products that contribute to decarbonization by customers—for example, carbon neutral steel and carbon neutral springs,*4 ; EV and CASE components; semiconductors and electronic components; and energy-related components—offshore wind power components in particular). We will contribute to the pursuit of decarbonization while growing our businesses by focusing on increasing orders received for products related to offshore wind power and products that contribute to a circular economy (e.g., magnetic sorters) as well as marketing metal powders such as soft magnetic powders (carbon neutral powders*5 for electronic components, including those for CASE applications).
- In the 4℃ Scenario, in which global measures to address climate change remain inadequate, the impact of transition risks would be limited compared to the 1.5℃ Scenario. However, we would enhance business continuity planning while maintaining and managing the supply chain by diversifying suppliers, maintaining appropriate inventories, and other measures, since underthis scenario, loss of plant facilities and products, supply chain disruptions, and other such incidents would be expected torise due to an increase in sudden natural disasters.
- In the face of climate change, we are studying and implementing various responses intended to mitigate risks and secure opportunities. These include efforts to achieve carbon neutrality and to gain entry intomarkets expected to experience growth due to climate change, andverifying the resiliency of business operations based on analyses of multiple scenarios.Going forward, we plan to promote various measures more effectively by updating and monitoring information related to these analyses.
- *4Steel bars and springs manufactured using CO2-free electric power
- *5Powders manufactured using CO2-free electric power
Risk management
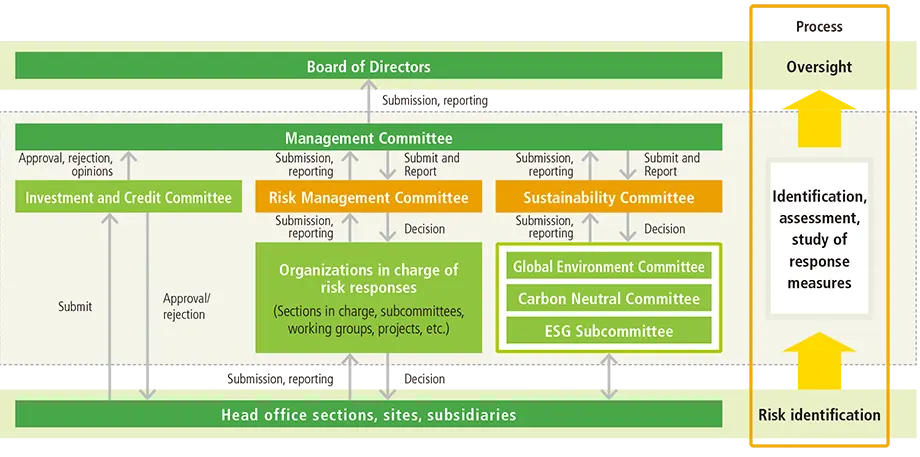
Climate change risk management structure
- Our basic structure for managing climate change risks consists of the Sustainability Committee, which manages transition risks, and the Risk Management Committee, which manages physical risks and other risks.
- Our risk management process involves identifying Companywide short-, medium-, and long-term risks; assessing these risks; and considering measures in response through discussions at the Risk Management Committee and Sustainability Committee under the supervision of the Board of Directors.
- The Investment and Credit Committee, led by the Corporate Planning Unit, reviews business plans and risks and deliberates on capital investments including those related to carbon neutrality.
- The Risk Management Committee formulates, verifies, and reviews business continuity plans (BCPs) to ensure that each section,site, and subsidiary can respond to and recover from natural disasters without delay.
Risk management structure
Indicators and Goals
For indicators and goals towards achieving carbon neutrality, please refer to "Efforts towards Carbon Neutrality."